Post Contents
- 1 Uttarabasti: A Unique Ayurvedic Therapy for Genito-Urinary Disorders
- 1.1 📖 Introduction and Definition
- 1.2 👩 For Females: Gynaecological Applications
- 1.3 👨 For Males: Genito-Urinary Applications
- 1.4 🔬 Mode of Action (Proposed Mechanisms)
- 1.5 🛠️ Components of the Basti Apparatus
- 1.6 Uttara basti:
Uttarabasti: A Unique Ayurvedic Therapy for Genito-Urinary Disorders
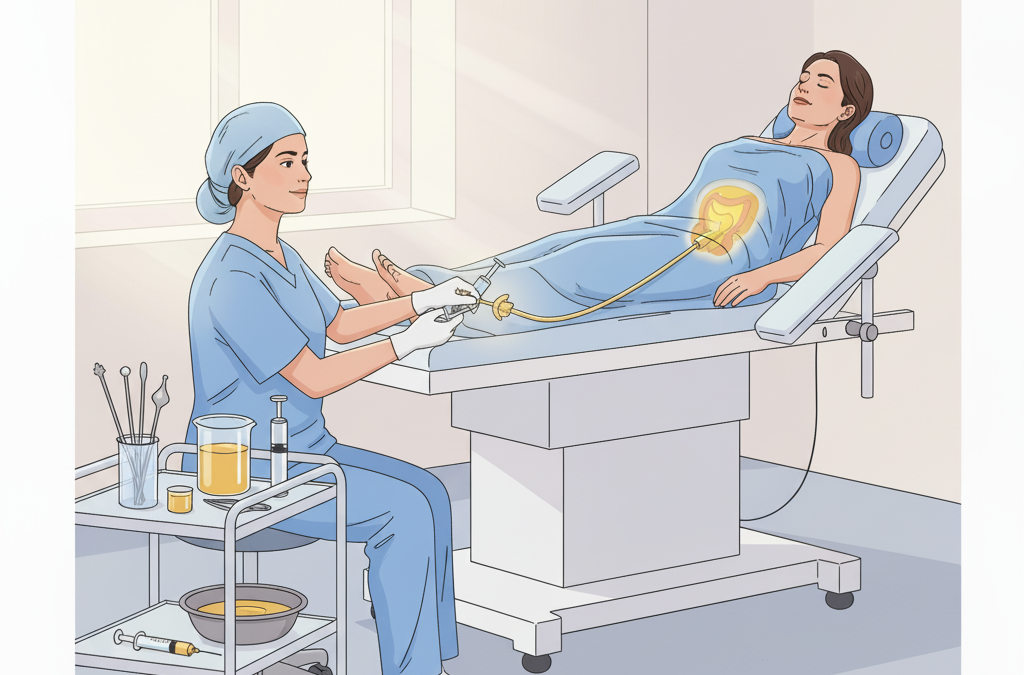
Uttarabasti (or Uttarbasti) is a distinct and highly effective therapeutic procedure within Ayurveda, holding significant importance in treating a variety of genito-urinary and gynaecological disorders in both males and females.
Best for female infertility related endometrium issues like over scratched or thickness etc. related issues Uttar Basti is the best treatment proven for many many patients.
Book Your Appointment for Treatment @ MsArogyam Ayurveda Call:: +91 9412637645 , +91 9219434343
📖 Introduction and Definition
The term Basti in Sanskrit is derived from Vas-Nivase, meaning “to stay.” Historically, the word Basti also referred to the urinary bladder, as the bladders of animals (like pigs, goats, or birds) were used as the container (Basti Putaka) for administering the medicated substance. Today, modern disposable syringes and thin cannulas are used for this purpose.
Definition
Uttarabasti is defined as the procedure where medicated substances (like Sneha—oils or ghees) are administered through the Uttarmarga (upper passage), which includes the vaginal route (for uterine/gynaecological conditions) or the urethral route (for urinary/seminal conditions). The results of this therapy are considered “marvelous” (Ch. Si. 9/50).
👩 For Females: Gynaecological Applications
In females, Uttarabasti is primarily administered via the vaginal route to deliver medicated Ghrita (ghee) or Taila (oil) into the uterine cavity (Intrauterine route). Ghrita is often preferred due to its superior property of Samskara Anuvartanat (retaining the properties of the medicinal decoctions it is processed with).
Timing (Kala)
Most Acharyas advise administering Uttarabasti during the “Rutukala” (post-menstrual period), as the Yoni Mukh (cervical os) is considered naturally open during this time (Ch. Si. 9/62).
Dosage (Matra) and Duration
The dose of Sneha (medicated oil/ghee) varies between different ancient texts:
| Acharya | Suggested Dose (Matra) |
| Acharya Sushruta | One Prasruta (approx. 96 grams/2 Pala), with freedom to adjust based on the patient and disease (Su. Chi. 37/106). |
| Acharya Vagbhatta | One Pala on the first day, increased gradually. |
| Acharya Charaka | Half Pala. |
| Sharangadhara & Bhavmisra | Two Pala. |
The recommended duration according to Acharyas Charaka and Vagbhatta is a cycle: administered for three consecutive days, stopped for three days, and then repeated for another three days continuously (Ch. Si 9/69).
Patient Position
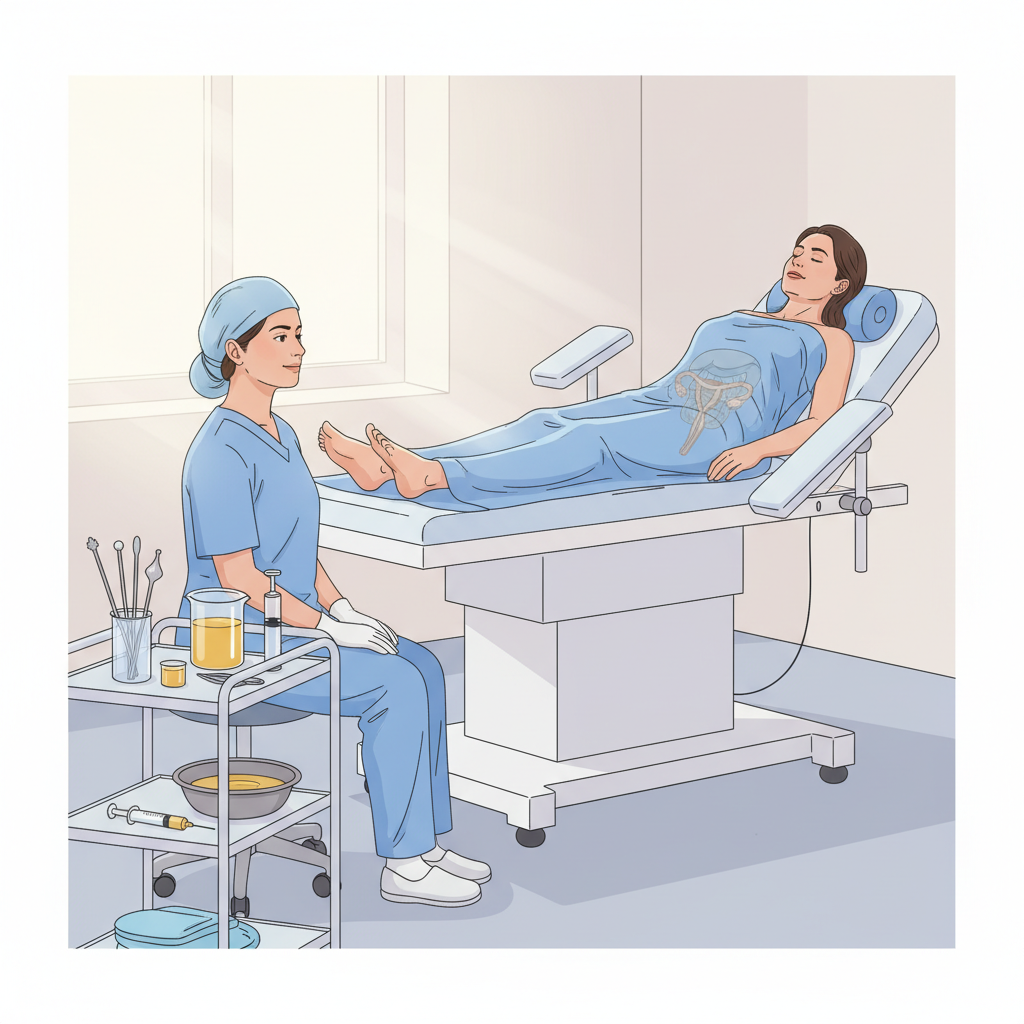
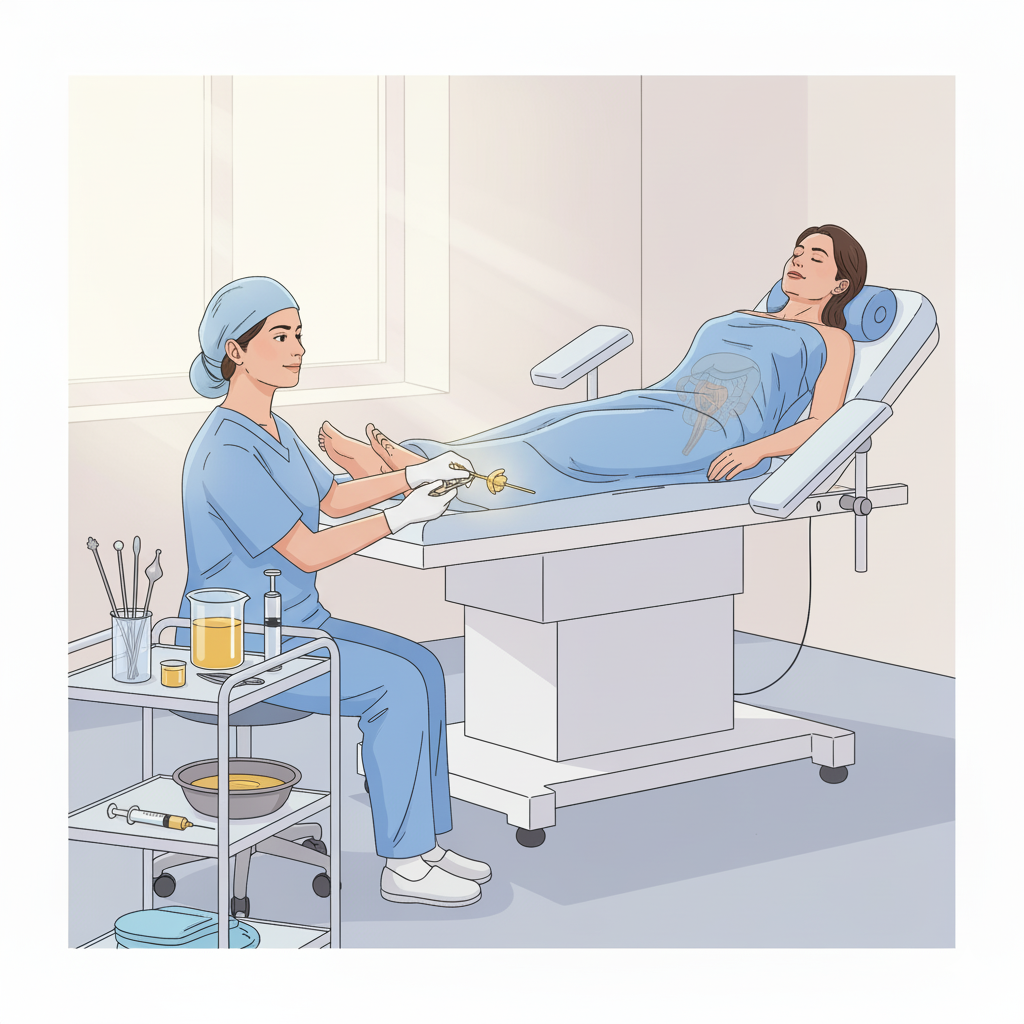
The patient should lie in the lithotomy position during the procedure.
Indications (Arha) in Females
Uttarabasti is indicated for numerous female reproductive and urinary disorders, including:
- Garbhashaya Gata Rogas (Uterine/Gynaecological disorders): Yoni Vibhramsha (Uterine prolapse), Yoni Shoola (Vaginal pain), Teevra Yoni Vyapat (Severe gynaecological disorders), Asrigdhara (Menorrhagia/Metrorrhagia), Anartava (Amenorrhea), Vandhyatwa (Infertility), and Apara Dwara Garbha Nirodha.
- Mootramarga Gata Rogas (Urinary tract disorders): Mootrakrichhra (Dysuria/difficulty in micturition), Mootrotsanga, etc. (Ch. Si. 9/62-65, Su. Chi. 37.125-126).
👨 For Males: Genito-Urinary Applications
In males, Uttarabasti is typically administered via the urethral route (Intra-urethral therapy). It is highly effective, especially in diseases related to the vitiation of Apana Vata Dosha (which governs the lower abdomen and elimination).
Indications (Arha) in Males
- Mootramarga Gata Rogas (Urinary tract disorders): Mootrakrichhra, Ashthila (Prostate enlargement), Vata Basti, etc.
- Shukra Gata Rogas (Seminal/Reproductive disorders): Shukra Doshas (Semen disorders), Shukrashmari (Semen calculus), Dhwaja Bhanga (Erectile dysfunction).
🔬 Mode of Action (Proposed Mechanisms)
The therapeutic action of Uttarabasti is attributed to both the local effects of the drug and its systemic absorption, particularly in treating infertility and genito-urinary issues.
Effect on Fertilization Factors
The procedure is believed to target the four factors essential for fertilization (Ritu-Kshetra-Ambu-Beeja):
- Ritu (Time/Ovulation): May correct abnormal hormonal functions required for ovulation.
- Kshetra (Field/Internal Genitalia): May correct pathological conditions in the internal organs, making them favorable for conception.
- Ambu (Nourishment/Circulation): Provides proper nutrition to the uterine mucosa via systemic circulation.
- Beeja (Seed/Ovum): May act on ovarian hormones, correcting ovarian dysfunctions.
Local Effects in Uterine Cavity
When administered into the uterus, the medicated Ghrita/Taila primarily acts on the endometrium, leading to:
- Lubrication: Softens and loosens uterine muscles and membranes, facilitating menstruation.
- Ovarian Stimulation: Local absorption or irritation may stimulate the ovaries to release estrogen and progesterone.
- Hyperaemia: Irritation of the uterine walls increases blood flow (hyperaemia), potentially causing thickening of the endometrial layer.
- Disinfection: The drug’s antiseptic properties help in disinfecting conditions like endometritis.
Mode of Action based on Modern Pharmacology
The action of Uttarabasti, particularly the absorption of lipid-soluble drugs like Ghrita/Taila, is supported by concepts from modern pharmacology:
- Lipid Solubility: Ghrita/Taila is highly lipid-soluble, enabling its high chances of absorption through the bi-lipid layer membrane of the bladder or uterine epithelium via diffusion.
- Endometrial Absorption: The endometrium, lined by epithelium, readily absorbs steroids and, possibly, active ingredients without significant local destruction.
- Receptor Binding: The endometrium contains Estrogen Receptor alpha (ER-α), the predominant subtype in the uterus. Estrogenic pre-substances in the medicated oil/ghee may bind to these receptors, enhancing estrogenic activity and resulting in proliferative and secretory changes leading to menstruation.
Intra-Vesical Therapy (Male/Urinary Route)
The modern medical parallel to urinary Uttarabasti is Intra-vesical Therapy, where medicines are instilled into the bladder via a transurethral catheter. Studies show that:
-
- The bladder urothelium, while designed for impermeability, can transport substances. The Ghrita/Taila’s lipid-solubility suggests high absorption through the urothelial bi-lipid layer.
- Absorbed portions may circulate systemically, reaching the sites of action (like the area of spermatogenesis to correct Shukra Doshas).
- The procedure itself stimulates the local organs and increases blood supply, favoring drug entry and waste product excretion.
🛠️ Components of the Basti Apparatus
Historically, the apparatus consisted of the Basti Putaka (container) and the Basti Netra (cannula).
Basti Putaka (Container)
Ancient texts mention using the urinary bladder of animals (sheep, goat, wild pig) or the neck skin of birds (gala charma tu pakshinam) for the Basti Putaka (Su. Chi. 37/107).
Basti Netra (Cannula)
The cannula used for administration varies based on the route and gender:
| Feature | For Males (Urethral) | For Females (Vaginal/Intrauterine) |
| Material (Dhatu) | Gold (Hema), Silver (Raupya). | Gold (Hema), Silver (Raupya). |
| Length (Deergha) | 14 Angula (Sushruta) or 12 Angula (Cha., Va., Sha.). | 10 Angula. |
| Depth of Insertion | 4, 5, 6, or 7 Angula (Ksharapani). Maximum is 7 Angula. | 4 Angula. |
| Tip Shape (Agra) | Should resemble Jati, Malati, or Karaveera Pushpa. | Pushpa Vruntopamatvam is not used. |
| Orifice (Chidra) | Allows Sarshapa (mustard seed) to pass. | Kechit Adhika (a bit wider). |
Uttarabasti remains a highly revered therapy for its targeted action and remarkable efficacy in treating complex genito-urinary and gynaecological disorders.
Uttara basti:
Uttarabasti, the unique procedure of Ayurveda, has great important in treating gynaecological disorders.
Introduction :
In Sanskrit terminology word Basti is derived from Vas-Nivase which means “to stay”. Word Basti also refers to urinary bladder. Bladder of pig, goat or birds, were used for this purpose in older days. but now a days 5 cc disposable syringe attached with a thin cannula is used for uttarabsati.
Definition :
Basti which is given through the uttarmarga that is through the vaginal route &results are marvelous is termed as uttarbasti. (Ch. Si. 9/50) ‘
Kala:
All the Acharyas have advised to administer it during the “RUTUKALA” because at that time yoni mukh is opened. (Ch. Si. 9/62)
Matra :
Acharya Sushruta has mentioned the matra of uttarbasti of sneha is one prasuta (2pala) he has also given freedom about matra, that according to patient and diseases, vaidya should adjust the matra (dose). (Su. Chi. 37/106)
Matra According to different acharyas:
Vagbhatta = One pala for 1st day after increased gradually
Sharangadhara and Bhavmisra = Two pala
Charaka = Half pala
Duration:
According to Acharya Charaka and Vagbhatta the uttarbasti should be given consecutively for threi days. But in this context, it has been said that sneha should be increased day by day for three days. There after, it should be stopped for 3 days| then again the uttarbasti should be repeated for days continuously. (Ch. Si 9/69)
Position: Patient should lie in lithotomy position.
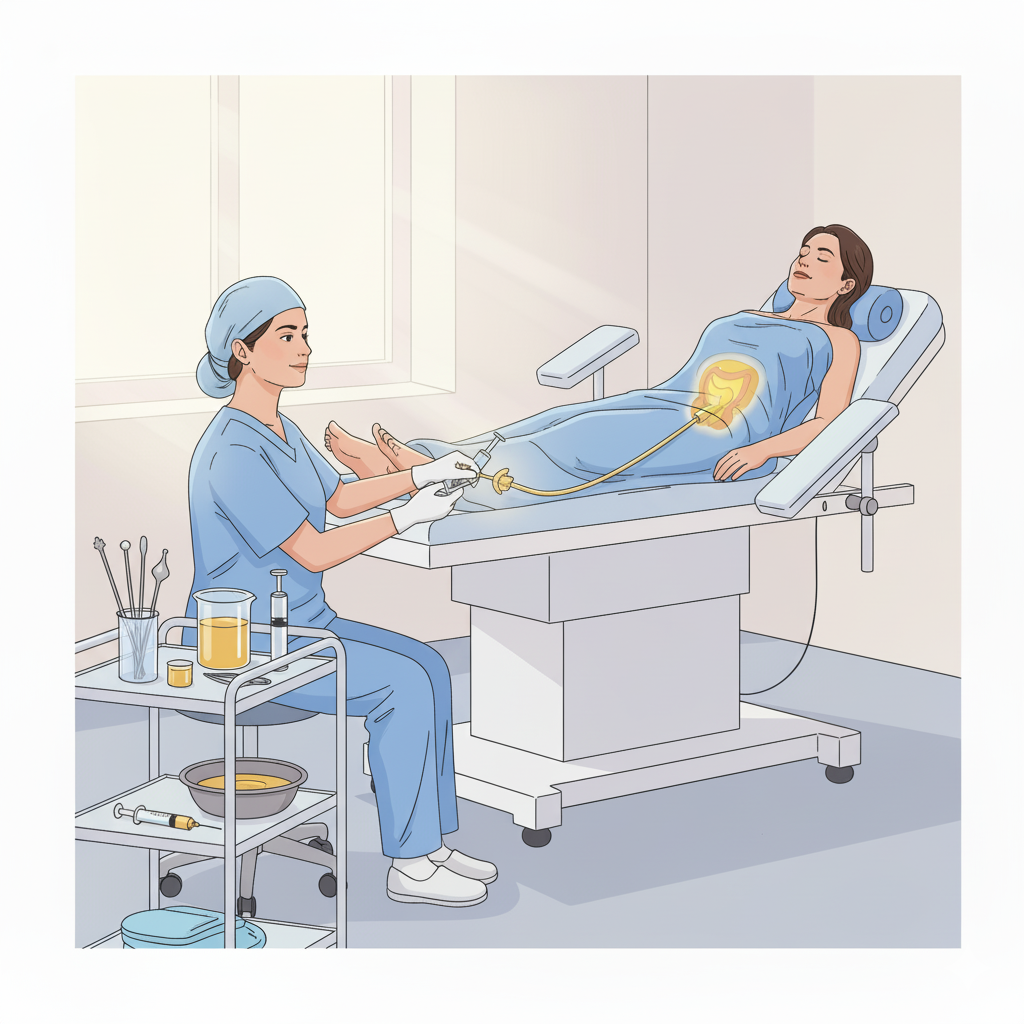
Intrauterine route :
By this route the medicated Ghrta/Taila is administered in uterine cavity through Vagina. Ghrta is best among Mahasneha due to “Samskara| Anuvartanat” (Ca. Su. 13/13). Due to Suksma Guna Sneha enters the microchannels (Srotas).The mucosal layer of cervix, uterus (endometrium) and fallopian tube is supplied with blood vessels and lymphatic spaces. It performs functions such as lubrication, ovarian stimulation, hyperaemia, as well as disinfections.
It consist of two parts
- basti putaka
- basti netra
Aurabhra shoukaro va api bastihi ajaha sa poojitaha
Tat alabhe prayunjeeta gala charma tu pakshinam(su. Chi. 37/107)
Basti of Mesha, Aja, Vanya shookara shouii be selected. If not available skin of birds neck should be used for the preperation of basti putaka
Purusha- Nirmana yogya dhatu:- Dalhana-Suvarnadimayam. Cha.si.9.50-51-hema,raupya Netra agra should resemble- Jati pushpa Malati pushpa Karaveera vruntagra s
Purusha:Nirmana yogya dhatu:-
hema,raupya Length-Chaturdashangula(Sushruta) Dwadashangula(Cha.Va.Sha) Antaha pravesha- shadangula
Ksharapani- Chatwari,pancha,shat sapta va ie 4/5/6/7 angula. Saptangulam cha param pranidhanam Himsyat
Shlakshna Gopuchavat moola(va) madhya sannivishta karnika Agra- Jati pushpa Chidra- Sarshapa nirgama Malati pushpa Karaveera vruntagra
Stree-Apathya marga Dhatu- Hema,Raupya Deergha- Dashangula Antaha pravesha-Chaturangula Sthoola- Medhrayama Chidra- Kechit adhika
Stree mootramarga- Dhatu- Hema,Raupya Deergha- Dashangula Antaha pravesha-Dwi agula(nari), Ekangula(Bala) Sthoola- Mootrasrotaha parinaha Chidra- Mudga vahis Agra-Pushpa vruntopamatvam to atra na yujyate (sa)
ARHA
Mootramarga gata rogas Garbhashaya gata rogas(Stree) Shukra dosha(Purusha)
Mootra marga gata rogas-Doshadhikyam avekshya etan mootrakrichhra haraihi jayet Bastim uttara bastim cha sarvesham eva dapayet(cha.si.9. 62)
Mootraukasada,Mootra jathara,Mootra krichra, Mootrotsanga, Mootra sankshaya, Mootrateeta, Ashthila, Vata basti, Ushnavata, Vatakundalika, Granthi, Vitvighata, Basti kundala,
Garbhashaya gata rogas
Yoni vibhramsha, Yoni shoola, Teevra yoni vyapat, Asrigdhara, Mootra aprasravana or Bindu bindu sravana,(cha, si ,9/62-65) Anartava, Akala rajah pravrutti,Apara dwara garbha nirodha,Vandhyatwa.(Su.Chi.37.125-126)
Shukra gata rogas- Shukra doshas, Shukrashmari, Shukrotseka, Dhwaja bhanga.ss
Effect of Uttarbasti :
We can assume the benefit of uttarbasti targeted on four factors of fertilization.
(i) Ritu: Means the ovulation time or period indicates proper hormonal functions necessary for fertilization, uttarbasti may correct the abnormal functions.
(ii) Kshetra: Means internal genital organs, many organic and pathological conditions of internal genitelia may not be favourable for fertilization so uttarbasti may be correct in condition.
(iii) Ambu: Means proper nutritional substance for the uterine mucosa, through the systemic circulation of the yoni.
(iv) Beeja : means the ovum. Uttarbasti may act on ovarian hormones and correct dysfunctions of ovary.
IN MALES:
Uttara Basti (UB) is a simple procedure of greater efficacy especially in the diseases concerned with Apana Vata Dosha. As Uttara Basti is indicated for the diseases of genito-urinary system, its site of action is likely to be on genito-urinary system.
Uttara Basti may be administered to achieve both local as well as systemic effects, So taking the relevant references from modern, the mode of action of Uttara Basti may be explained as follow as.
stimulation of medra: Intraurethral therapy has an specific role to play in the erectile dysfunction by stimulating the penis (medra) which is the mula sthana of shukravahasrotas and thus increases the sexual desire.
EAREST ROUTE OF DRUG DELIVERY
Intra-vesical therapy is the direct reference of UttaraBasti in modern medical science. Instillation of medicines into the bladder by transurethral catheterization is known as intra-vesical therapy.
As the mammalian bladder functions as reservoir for hypertonic urine, it must be impermeable to water. Although the structural features of urothelium support the concept of impermeability, the physiologic experiments suggest otherwise. Ultra structural studies have shown that the lumen of the bladder is lined by the transitional epithelium, composed of at least three cell layers.
The inner most layer of the urothelium is formed by the basal cells attached to the basement membrane. An intermediate layer consists of larger cells containing lysosomes and numerous cystoplasmic vesicals. The most superficial apical layer is composed of large hexagonal cells containing microfilaments and covered with glycocalyx. Urothelial impermeability has been inferred form the presence of tight junctions between adjacent apical cells.
Studies have proved that the volume and composition of urine were altered when left in the bladder for 12 hours compared with hourly voiding. Instillation of amino acids into the bladder produces an increase in concentration gradient form the mucosal to the serosal surfaces. Sodium and amino acid gradients suggest that mechanisms exist for transport of substances across the urothelium.
In vitro data demonstrates that, the mammalian bladder possesses active ion transport system. Although apical epithelial cells in the bladder are impermeable to water but they actively transport sodium by means of various channels. Disruption of the polysaccharide layer covering apical cells, increase permeability to urea and has been linked to inflammatory or hypersensitivity disorders of the bladder. It is also possible that other substances such as prostaglandins have a cyto-protective role and effects urothelial permeability. Human bladder mucosa synthesizes a variety of prostaglandins that may influence bladder.
A consensus has not been reached regarding the physiologic role of active ion transport mechanism in the bladder. One function may be in the epithelial cell volume regulation during changes accompanying distension. Because, ion transport can occur in several directions; another role for this process may be active maintenance of urine hyper-tonicity. The extensive vascularity of the sub epithelial region of the bladder has been used as the evidence for this hypothesis. Epithelial permeability could provide a mechanism for exposing smooth muscles to intra vesical contents, there by altering the bladder contractility.
Investigators have demonstrated that intra vesicle instillation of anti-neoplastic drugs, anticholinergic drug agents and calcium channel antagonists influence detrusor muscle Unction and access systemic circulation. A better understanding of urothelial permeability may explain such disorders as interstitial cystitis and how substances are excreted in the urine or administered intravesically to influence the bladder sensation and the contractility. These experiments provide sample reference for the action of the bladder epithelium. Thus based on the above experimental findings a hypothesis can be made that that since the Ghrita/Taila is basically a lipid soluble its chances of getting absorbed through bladder epithelium which is also a bi-lipid layer membrane is very high through the process of dif^sion. As a result the absorbed portion of the Ghrita/Taila may circulate through blood and may reach the site of spermatogenesis and correct it.
The Uttarabasti procedure may itself stimulate the organs and also increase the blood supply. The increasing blood circulation may favours entry of drugs and excretion of waste products from cell providing necessary elements to the organ facilitating Bijanirmana.
When Ghrita/ Taila is administered locally in uterine cavity, it is primarily absorbed by the endometrium. Here in it performs functions such as lubrication, ovarian stimulation,hyperaemia, as well as disinfections.
Lubrication :
It has been recognized as a universal lubricant. On administration it tends to soften and loosen the uterine muscles and membranes. Thus making them more motile as an effect it helps to break down the endometrial layer and facilitate menstruation.
Ovarian stimulation :
During the process of Uttarbasti, some amount of the Ghrita/Taila enters the ovaries through the uterine wall. This in-turn stimulate the ovaries to release progesterone and oestrogen. On account of local irritation. These two hormones thus cause the onset of menstruation.
Hyperamia:
The medicated oil reaching uterine cavity causes irritation of its walls. This leads to the condition of hyperamia which causes thickening of the endometrial layer.
Disinfection :
The test drug contains many antiseptic agents therefore it causes disinfection in conditions of endometritis etc.
Probable made of action of Uttarbasti
according to Modern Pharmecology Uttarbasti is a unique therapy in Ayurveda Uttarbasti is Shodhana chikitsa. It has a marvelous result in Gynaecology disordrers. Probable mode of action of uttarbasti it is mentioned as according to modern science, its seems to be very tuff task. But efforts as follows could easily be made for performing uttarbasti.
Absorption of Drugs depends upon,
- Techniques of Administration
- Drug
- Endometrium
- Techniques of Administration.
- Route of Administration.
The route of administration exerts a considerable influence upon the activity of hormone preparation certain hormones are ineffective when given by mouth while others are highly effective. Steroids are comparatively readily absorbed without much local destruction by the surface epithelium.
The local administration of hormone preparations has the additional advantage that comparatively small doses are suffice to produce definite effects. This has often been used to advantage in bioassay techniques. Thus extremely small doses of luteoid hormone can be detected, by the local progestational proliferation in the rabbit endometrium, when they are directly applied to it.
-
The Solvent
The Solvent in which hormone is parentearlly administered plays an important role in determining its efficacy. It has been shown that the folliculoids can be absorbed selectively from oil.
-
Drug
Drug is most important in treatment. Effectiveness of drug is depends upon its.
- Lipid Solubility
- Molecule
- Presence of receptor
- Charge ions
-
Endometrium
Endometrium is second important thing for consideration endometrium having lining epithelium, epithelium absorbed estrogen without much local destruction. All hormones act through receptors on the cell, surface in the case of estrogen, two receptors have now been identified the first is now designated as estrogen receptor alpha (ER – a) and the more recently identified another one as estrogen receptor beta (ER – 6). ER – a is the predominant subtype in the uterus and pituitary. ER – 6 seems to be a weak Transactivator. It is present in significant numbers in the ovary. (Jeffcort’s Principles of Gynaecology). It is also assume that the end organs of estrogen stimulation such as the Uterus transform the estrogen into other products in a process intimately
linked with the biological utilization of these hormones. Indeed invitro experiments indicate that uterine tissue will modify the structure of the estrogen molecule. Thus, Heller incubated estrogen with rat and rabbit uterine tissue and observed an increase in estrogenic potency. [Heller, C.G. ENDOCRINOLOGY – 1940]
The elaboration of hormones is also depends upon local blood flow endomentrium having the high amount of circulating blood. In view of the above facts, probable mode of action considers could be as follow probable mode of action. Now it is known that endometrium having major role in Hormonal
Administration.
Endometrium having ER – a Receptor of Estrogen. Estrogenic presubstance of Arkapushpa Taila bind with receptor and form complex. These complex enhance the estrogenic activity in endometrium due to this activity enhance in proliferative and secretory phase of endometrium occurs which finally result in Menstruation.






